PORTFOLIO

sChrono

About The Project
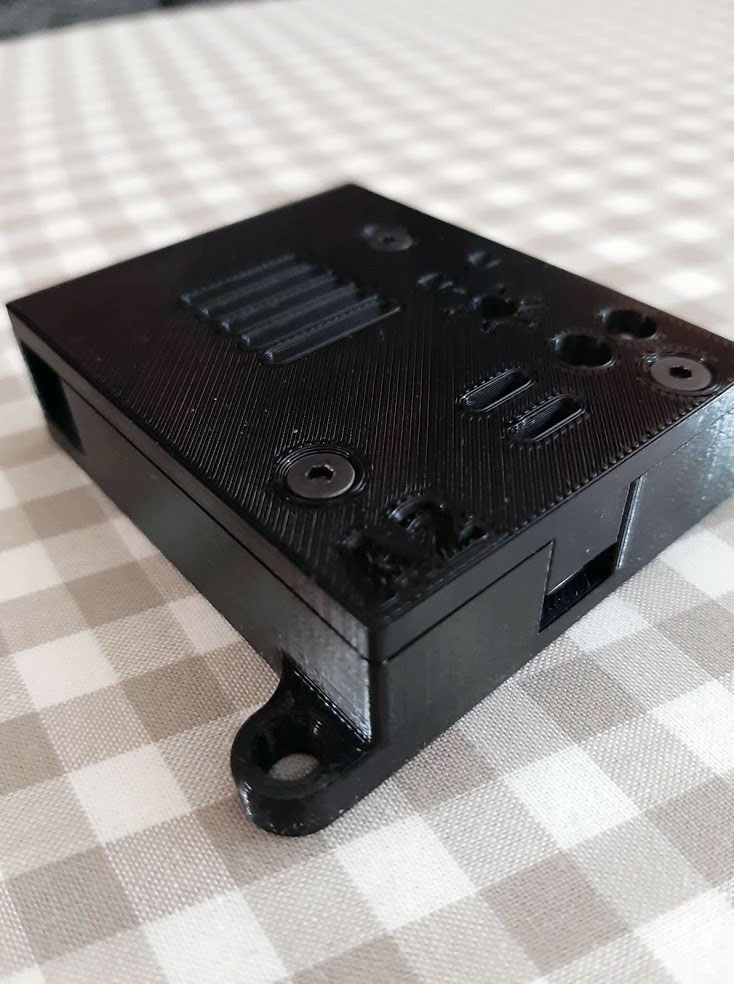
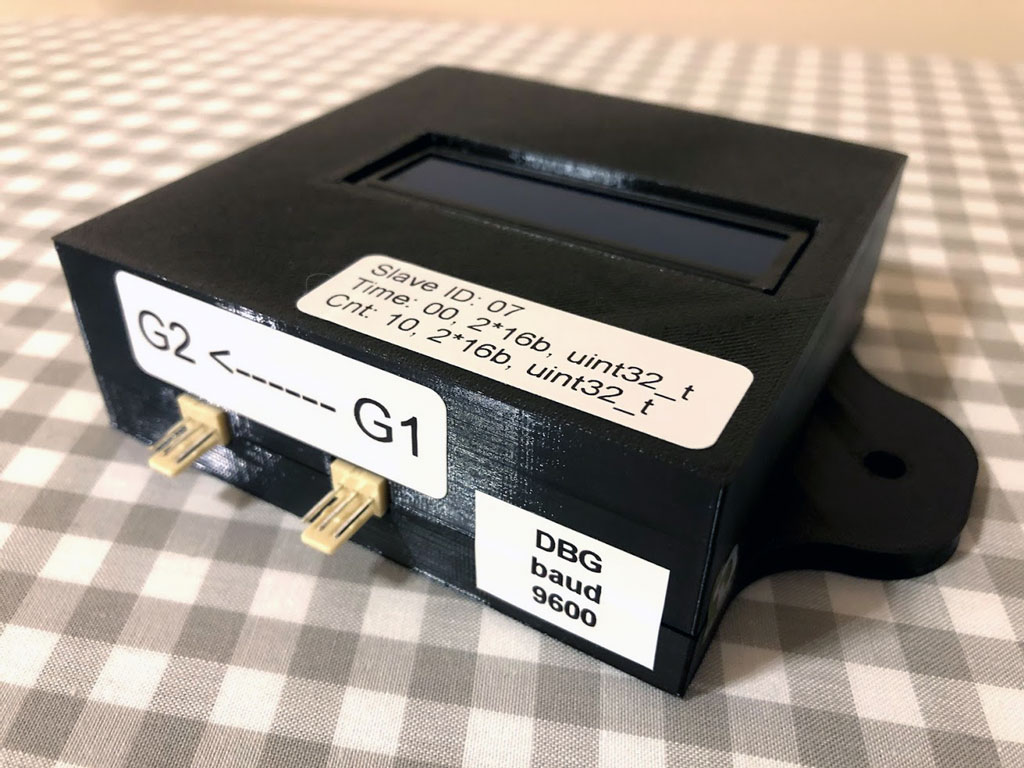
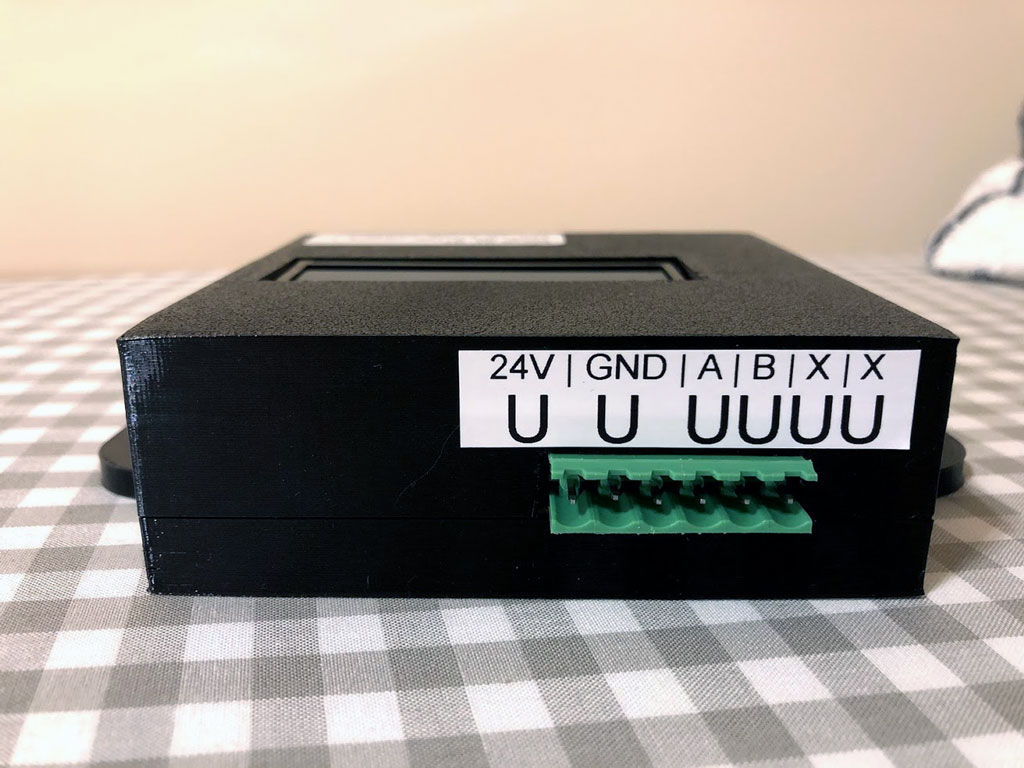
I have designed, built and programmed a prototype of the device that allows measuring very short periods of time with 1 microsecond resolution.
It’s being used as a part of a system that measures speed of automatically launched projectiles passing through optic gates.
It communicates via Modbus RS485 interface with Delta PLC industrial controller. Customer uses it for machines that are testing mechanical strength of modern PV panels.


SKYLIGHTS

About The Project
I have designed, built and programmed a prototype of the device that manages “smart” lightning integrated with furniture. The main idea was to use it in kitchen – devices can work independently and can drive long strings of LEDs with very smooth PWM animations, they have PIR and proximity sensors, can be used with drawers and lockers without the need of mechanical switches. Devices can handle custom animated light profiles, which makes possible e.g. highlighting wardrobe’s insides for a few seconds and then gradually dimming the lights, also turning the power off in case of longer inactivities.

DPDK (Open Source)

About The Project
Data Plane Development Kit is an Intel’s open source project that extends an idea of using polling dedicated CPU cores instead of interrupt-driven networking to speed operations by a huge numbers. For more information I’d suggest taking a look at project’s main page: https://www.dpdk.org/
My role in the project was Network Software Developer. I was mostly working on DPDK’s small part called “QAT”, which is an API for Intel hardware called Quick Access Technology supporting on-chip cryptography and compression.
To see my contributions to the project (including code I wrote), check out the Patchwork webpage:
http://patchwork.dpdk.org/project/dpdk/list/?series=&submitter=1184&state=*&q=&archive=both&delegate=
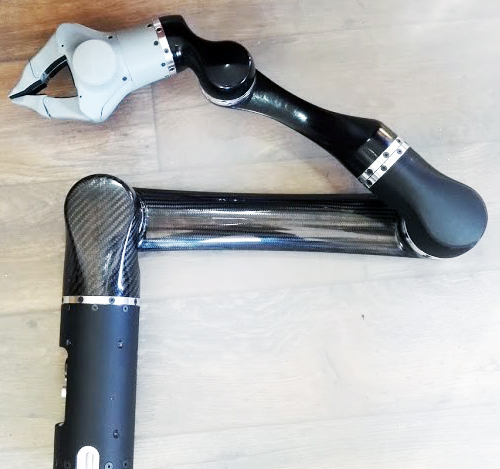

L2R Robotic Arm

About The Project
Main goal of the project is to design and build a robotic arm, with very integrated mechatronics, configurable kinematics and, prefferably, unlimited number of rotations in each joint.
My tasks, as part of L2R, included:
- high- and low-level system architecture design,
- design and development of miniature motor controller with additional “smart” functionalities,
- development of industrial grade internal interface, based on EtherCAT,
- co-design and development of mechatronic system for sending electrical signals via rotating mechanical parts,
- software development with GUI for PC user (Linux, GTK+).
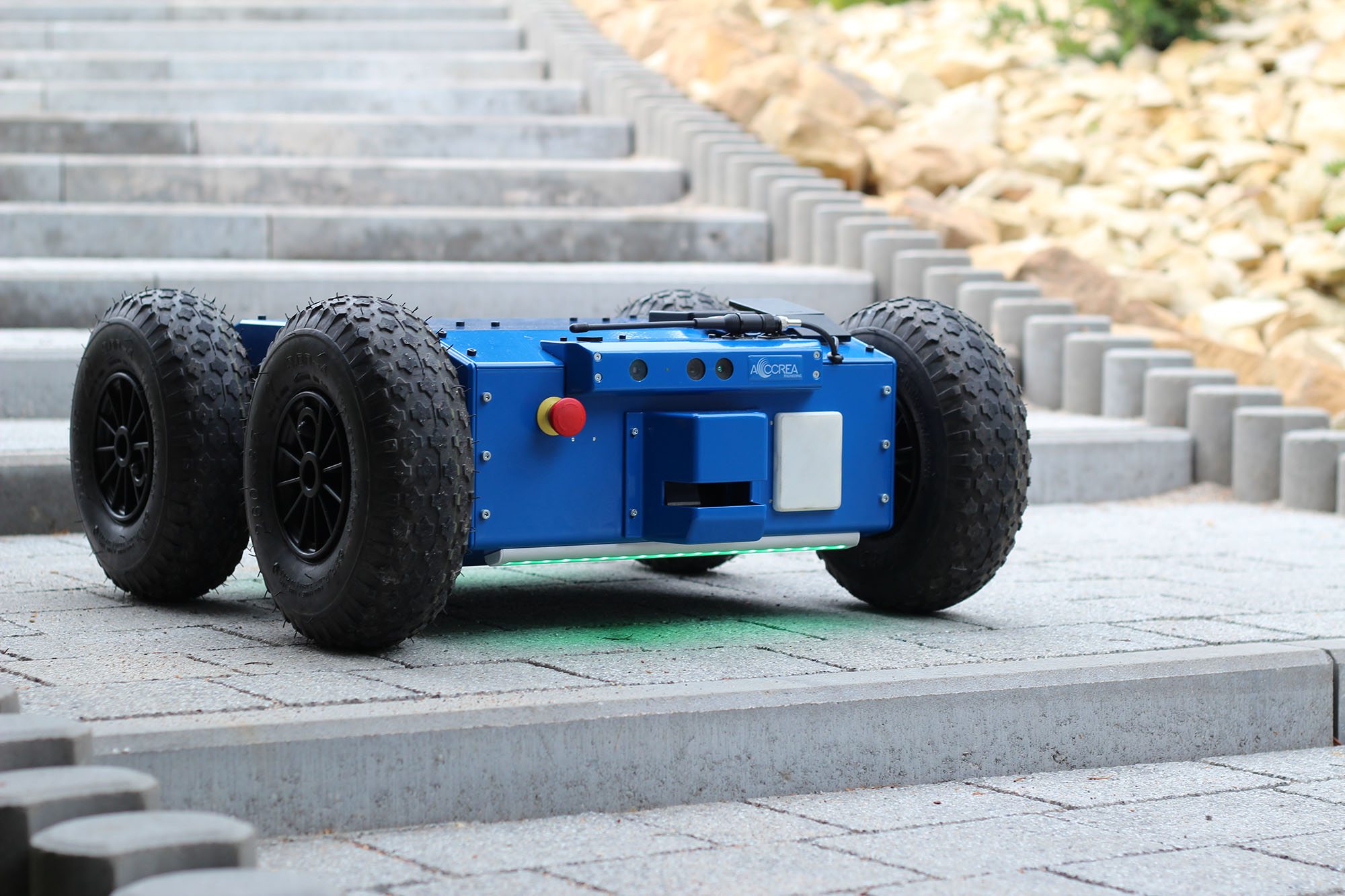

SKIDDY Mobile Platform [2015-2018]

About The Project
The project consisted of building a universal, resistant to difficult working conditions (rain, snow, mud, high dust, etc.) mobile platform with a lifting capacity of 100-150 kg.
My tasks, as part of SKIDDY, included:
- design and implementation of the SkidController controller, reducing the costs and increasing the hardware integration factor for controlling 4 high-power motors,
- cooperation with mechanical designers on the drive design and efficient cooling for dust-tight and watertight robot housing,
- high-level software and ROS libraries integration to facilitate the use of the robot’s capabilities to the customer.
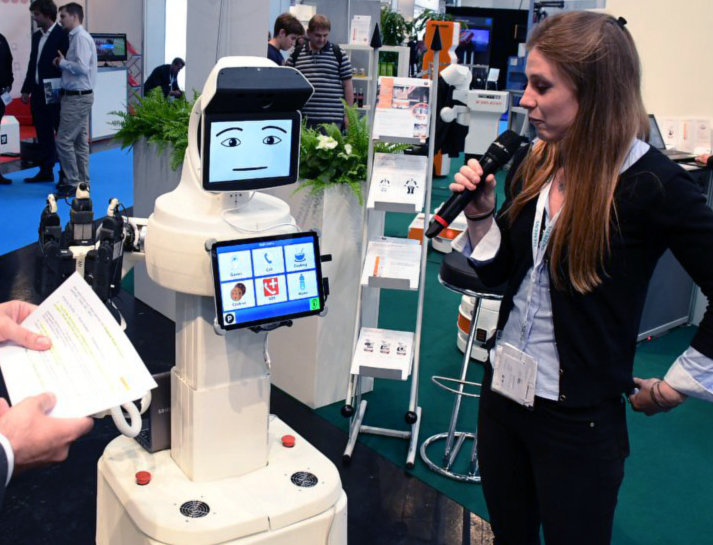

RAMCIP – Robot Assistant for MCI Patients [2014-2017]

About The Project
The project involved building a robot that would autonomously supervise and support elderly people and those with mild cognitive impairment (eg the onset of Alzheimer’s disease).
The robot’s tasks include: detecting the patient’s fall and immediately informing the doctor, supervising the hob while cooking lunch and switching off the burner, if the user forgets about it, administering medicine, helping in reaching objects from hard to reach places (eg high shelves), initiating teleconferences with the patient’s family, periodically carrying out psychological tests – to track the development of the disease.
My tasks, as part of RAMCIP, included:
- co-writing of a project application for Horizon2020 (grant 643433),
- software development for embedded (STM32) and PC (Linux+RT_PREEMPT) systems in C/C++,
- further development of JointsController, which I have designed for ReMeDi project,
- planning, supervising and work reporting of electronics designers and programmers team,
- representing the company in front of the consortium in all the topics related to the system architecture and user safety issues,
- co-creation of the robotic arm control system,
- design and co-creation of the mobile platform control system, prototyping and testing.
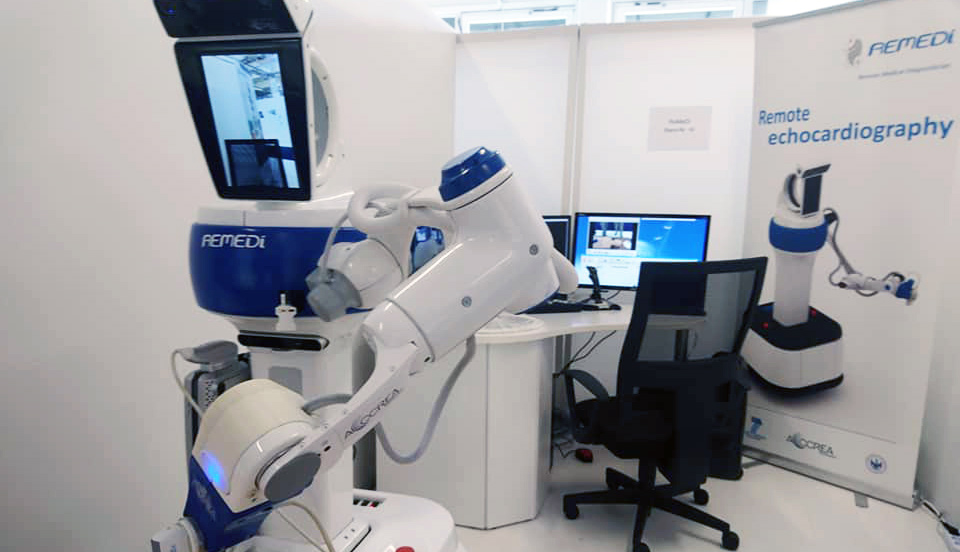

ReMeDi – Remote Medical Diagnostician [2014-2016]

About The Project
The project’s main goal was to build a robot with control station, that allows remote (online) USG and palpation examination, using haptic interface. ReMeDi robot is a kind of “extension” of doctor’s body, which enables him to move around the patient and to feel all the forces acting on robot’s arm.
My tasks, as part of ReMeDi, included:
- design, implementation and programming of the JointsController (STM32), which replaced the previously used ControlBox (PC); the robot would be too big, too expensive and would have a very limited battery life without it,
- planning, supervising and work reporting of electronics designers and programmers team,
- representing the company in front of the consortium in all the topics related to the system architecture and user safety issues,
- co-creation of the robotic arm control system,
- design and co-creation of the mobile platform control system, prototyping and testing.


FREEbot – Freescale tribute robot

About The Project
Similarly to the “Orangutan” robot, FREEbot was meant to encourage customers to buy specific robotic components from online shop I was working for. It is based on very popular FREEDOM-KL25Z, which could be event received for free at some point. Freescale’s innovation was Code Warrior with Processor Expert tool, which allows user to configure most of the peripherals with beginners-friendly clickable forms.
FREEbot consists of cheap parts, including Pololu KTIR transoptors, Pololu step-down regulator and Arduino motor shield (L298 + Schottky diodes). Sales of those parts skyrocketed a week after publication of my “Step by step guide – how to build FREEbot”, which you can find here.

ORANGUTAN – Thinking Robot

About The Project
The main goal of this project was to design and develop a small and cheap robotic platform, that would encourage customers to buy specific robotic components from online shop I was working for.
It uses Pololu Oragutan controller (AVR) – hence the name -as well as some other Pololu parts and miniature servomotor.
Double SHARP sensors measure distances for a obstacles and the differential measurements are being used for P-like (proportional) controller to adjust the robot course.


